v-50 ballistic impact test|ballistic testing of armor : discount store 3.8 Ballistic limit, protection criteria (V 50 BL(P)) . The V 50 BL(P) may be defined as the average of an equal number of highest partial penetration velocities and the lowest complete . Videocam Volume_Off 22 Secs - Rule 34 XYZ
{plog:ftitle_list}
25 de fevereiro de 2024 - Português. 21:30 Comprar. Ingressos online disponíveis, escolha um horário para comprar. Descubra todos os sessões e horários disponíveis para o .
v50 ballistic limit
Perforation performance of body armor is typically evaluated by V50 ballistic limit testing. Shot velocities are sequentially controlled by a up/down method to populate a sample containing results on both sides of the true value of the V50 velocity.
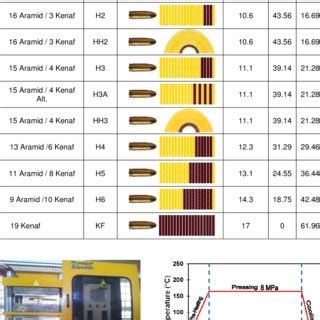
Table 7 shows the ballistic test requirements for each of the five (5) test .
3.8 Ballistic limit, protection criteria (V 50 BL(P)) . The V 50 BL(P) may be defined as the average of an equal number of highest partial penetration velocities and the lowest complete .The most common metric of ballistic performance is the V-50, which refers to the projectile velocity that has a 50% probability of completely penetrating the target (an average calculated .
Table 7 shows the ballistic test requirements for each of the five (5) test projectiles in terms of specification revisions, armor plate thickness ranges, mathematical models, and security ."V-50" or" Velocity-50%" - is a ballistic test where bullets are fired at higher and higher velocities until they start penetrating. The velocity of the bullets where 50% of the bullets DON'T . As described above, a V-50 test is the most common way of quantifying the ballistic performance of a system. However, for complex armour systems, in which the .The protection V 50 ballistic limit is defined as the average of 6 fair impact velocities comprising the three lowest velocities resulting in complete penetration and the three highest velocities .
ballistic testing of armor
Central to this task is a complete and thorough understanding of the so-called “V-50” test – well known but neither well understood nor appropriately applied. A comprehensive .Specifically, we present simulation results for the ballistic limit (V50) of IM7/8552 composite panels ballistically tested with an impactor representative of a high-velocity fan-blade-out .ballistic impact response of non-backed woven aramid fabrics is studied by considering 4-sided, circular, and diamond clamped fabrics with cross-sectional areas varying between 5 cm 2 and .
and highest non-penetrating shot velocity (VNP) such that VP
The entirety of the aforementioned finite element studies of fabric impact are deterministic and therefore incapable of generating a ZMR and a V 0-V 100 curve. These deterministic models cannot shed light on how sources of material, geometry, and testing variability that are inherent in all composite fabric armor systems affect the probabilistic .
Beyond the logistic regression modeling of empirical V 50 test results, there are theoretical methods for considering the influence of material properties on ballistic performance [14–19]. . energy dissipation away from a point of ballistic impact, and the specific toughness represents the approximate amount of elastic energy a fiber can .impact which in turn result in inconsistent V50 values. In some cases a shatter gap could exist. Shatter gap is a condition where the same armor plate will have two V50 ballistic limits, with differences greater than the 150 ft/sec spread allowed in determining the V50. Shatter gap occurs because the projectile core Per the test methodology, a helmet is placed over the clay-filled headform. RTP (or V 0 testing) is then conducted as a sequence of five ballistic impacts, one each to the front, rear, left, and right sides of the helmet, and the helmet crown ().Internal Operating Procedure IOP PED-003 specifies the precise requirements for the five impact locations for V 0 9-mm RTP/BFD .
A woven aramid (Kevlar®)/polyvinyl butyral phenolic composite that is used in ballistic applications was subjected to a wide variety of characterization and ballistic impact tests. Characterization data obtained under various stress states were used to generate two different models of the composite. The first model utilized a mesoscale modeling approach. . The ballistic test standards manufacturers used are (1) NIJ-STD-0106.01 Type II and (2) V 50 requirement of the US military specification for PASGT Helmet, MIL-H-44099A. The NIJ-STD-0106.01 is a standard developed by the Law Enforcement Standards Laboratory of the National Bureau of Standards to establish performance requirements and methods of .
This chapter presents different classifications of ballistic impact, projectile shape and target; impact response of materials under ballistic impact at different strain rates and striking velocities. Thes e include the V 0, V 50, and V 100 ballistic limit vel ocities and are designated as the maximum veloci ty at which no complete penetration will occur, the velocity at which a 50% probability .
Based on these results, the V 50 ballistic limit of the ACH was determined as 678 m/s at the front impact location. This V 50 ballistic limit from simulation matched well to experimental data, i.e., 689 m/s; . In the second validation of the FE model using the V 50 ballistic limit test, the simulation results were shown to have good agreement .
ballistic test instrumentation
Utilising our fully equipped, indoor ballistic and impact laboratory, PBL offers a full suite of ballistic testing capabilities across a full spectrum of industrial, defence and civilian test standards. . MIL-STD-662F: V 50 Test for ballistic armour. EN 1063/1522: Security Glazing – Testing and Classification of resistance to ballistic .Effects of fabric target shape and size on the V 50 ballistic impact response of soft body armor Gaurav Nilakantan1, Steven Nutt1,* 1. Mork Family Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, M.C. Gill . The impact test setup, including the particulars of the fabric material and weave, and projectile has already been described in . In this paper we report findings from ballistic experiments conducted on Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) flat panels. We measured ballistic limit velocities, V 50 of panels of different thicknesses using a fragment simulating projectile (FSP) and characterized back face deformation (BFD) using a spherical projectile. UHMWPE panels with . 4.2. BALLISTIC TESTING METHODOLOGY. The helmet ballistic testing methodology has been derived from existing body armor testing methods. The methodology for ballistic testing for body armor follows from testing done in the late 1970s by Prather et al. (1977) that, however tenuously, connects the current body armor methods and the test .
The protection V 50 ballistic limit is defined as the average of 6 fair impact velocities comprising the three lowest velocities resulting in complete penetration and the three highest velocities resulting in partial penetration. The sample test window size is 50.8 mm by 50.8 mm. . Ruggeri, C. R., Emmerling, W. C. & Altobelli, D. J. Ballistic impact testing of aluminum 2024 and titanium 6Al-4V for material model . These bullets are designed to expand upon impact with soft tissue. The expansion deforms the bullet and increases its diameter which creates a larger and more effective wound channel. . Ballistic Test Results.380 ACP Ballistic Gelatin Tests. . Liberty Ammunition 50 gr Civil Defense: 9.32: 0.388: 1342.6: Remington 102 gr Golden Saber: 19.46 .DOI: 10.1016/J.DT.2018.03.001 Corpus ID: 139194366; Virtual ballistic impact testing of Kevlar soft armor: Predictive and validated finite element modeling of the V 0 - V 100 probabilistic penetration response
The ballistic test standards manufacturers used are (1) NIJ-STD-0106.01 Type II and (2) V 50 requirement of the US military specification for PASGT Helmet, MIL-H-44099A. The NIJ-STD-0106.01 is a standard developed by the Law Enforcement Standards Laboratory of the National Bureau of Standards to establish performance requirements and methods of .
Ballistics testing is a standards-based process, where products are tested via a certified impact test of different ammunition types to determine if they meet protection, safety, and performance criteria. . The number of layers used to make a bulletproof jacket ranges between 10 and 50 and weighs . Fig. 3.5 shows the ballistic impact on .specimens and impact test articles. This report focuses on one of these four efforts, the ballistic impact testing for model validation. The report describes impact testing which has been done on aluminum (Al) 2024 and titanium (Ti) 6Al-4vanadium (V) sheet and plate samples of different thicknesses and with different types of projectiles, oneA REVIEW OF THE V50 BALLISTIC TEST REQUIREMENTS OF MIL-A-46100 Objectives The objectives of this memorandum report are twofold: * To provide the analyst with the various revisions and amendments of the V,6 ballistic limit requirements of MIL-A-46100 for the purpose of making easier and more accurate analyses and . Post-test exemplary non-penetrated fabric target: V i ¼ 119.75 m/s (a) strike face (b) rear face (as a reference scale, note the yarn span is 0.747 mm).
Fig. 1 Ballistic Impact Test on Composite Plate 2.3 Determination of Ballistic Limit. The V 50 ballistic limit velocity for a material is defined as the velocity for which the probability of penetration of the chosen projectile is 50%. This value is found by performing six ballistic impact
army ballistic approval test
how to test hardness of pool water
19 de jan. de 2024 · Bet Vencedor Aposta - Jogatina Diariaaviator robomaleta de poker 500 fichascasino poker chipsThe Magic Cauldron. Antes de iniciar o processo de declaração, é importante compreender quais são considerados rendimentos extras e como identificá-los. Além dos rendimentos provenientes do trabalho formal, são considerados .
v-50 ballistic impact test|ballistic testing of armor